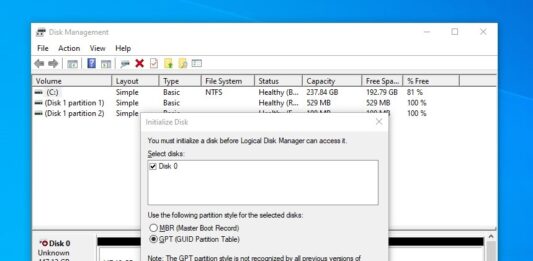
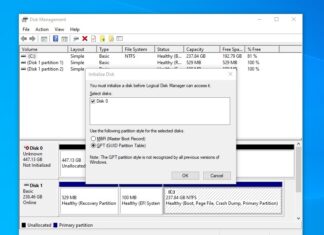
MBR vs GPT – Partition Table Explained
When you plug in a newly-purchased HDD or SDD to the computer, the operating system will often ask you to initialize the disk. Have you ever wondered what the differences between MBR and GPT?...
RAM Disks Explained
It is now common to see NVMe SSDs to reach speeds over 3 GB/s, or upwards of 6 GB/s for PCIe Gen 4 drives. With RAM disks, you can even get more storage performance...
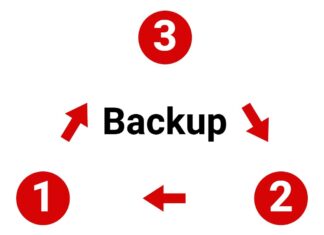
The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy Explained
Data backup is extremely important for everyone, especially when we keep almost everything digitally in this age. Whether it is a hard drive or solid-state drive, accidental damages and malfunctions are hard to prevent....
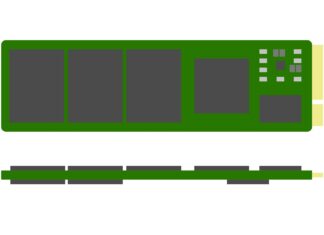
M.2 SSD Form Factor Explained
In recent years, the more compact M.2 form factor solid-state drives have taken over the traditional 2.5-inch in the market for high-performance storage. M.2, previously called Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is designed to...
USB Standards (Universal Serial Bus) Explained
Universal Serial Bus or USB has become the most widely-adapted industry standard over the past couple decades, since its first release in 1996. USB is constantly being updated and maintained by the USB Implementers...
Monitor Curvature Explained
Curved monitors have become more wide spread, whether they are a gaming-oriented displays or large 4K televisions. Based on your desk setup and preferences, you may want monitors to have slightly different curvatures. But...
Universal Flash Storage (UFS) Explained
What is UFS? UFS or Universal Flash Storage is a newer flash memory specification, with the intention to replace the slower eMMC (embedded MultiMedia Card) standard. It is designed by JEDEC, and was first...
LGA vs PGA – CPU Socket Types Explained
For the past decade, there are two major industry leaders in the CPU market, AMD and Intel. Customers always compare their technologies used in products, arguing which side is better. One of the most...